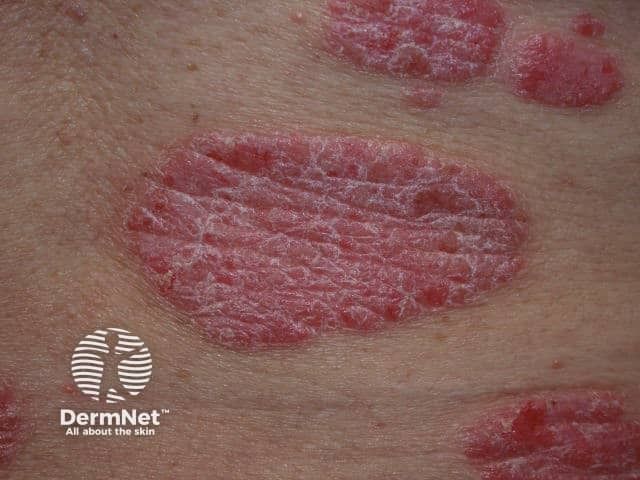
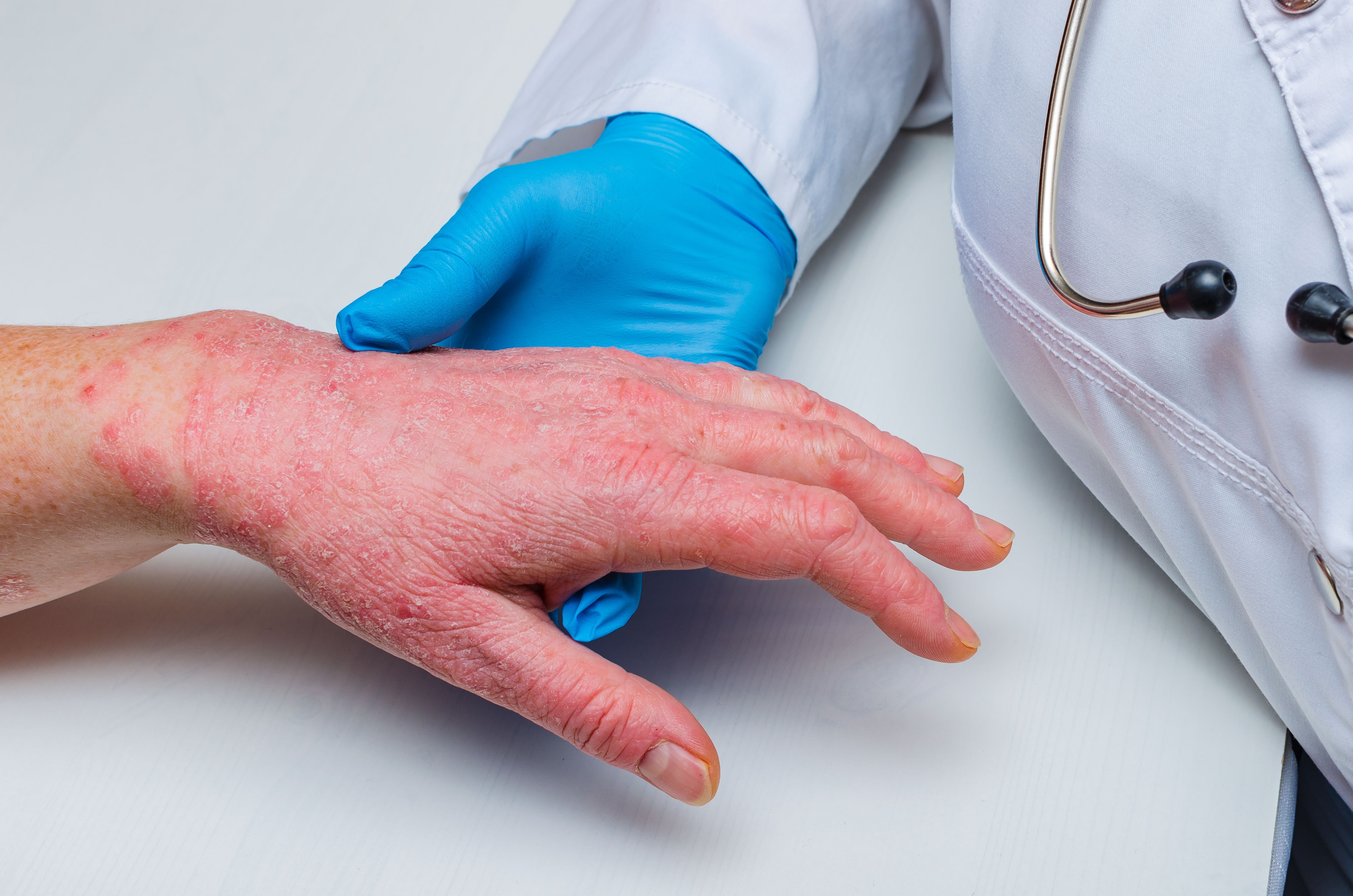
Psoriasis
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
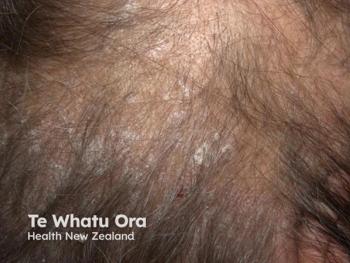
Discover the promising results of risankizumab for treating genital and scalp psoriasis, showcasing significant improvements in symptoms and quality of life.
New research reveals a promising strategy to slow type 1 diabetes progression by targeting inflammation with an existing psoriasis drug.
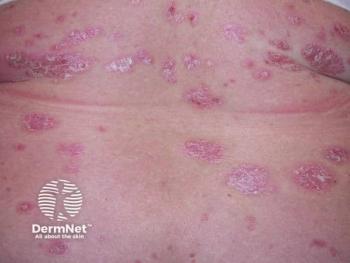
Abrocitinib’s targeted inhibition of JAK1 offers effective control of AD, but may, in rare instances, lead to a shift in immune expression resulting in paradoxical psoriasis.

Johnson & Johnson's icotrokinra shows promising results in treating moderate plaque psoriasis, especially in challenging areas like the scalp and genitals.

The promising safety and efficacy results were presented at the Society for Investigative Dermatology 2025 Annual Meeting.
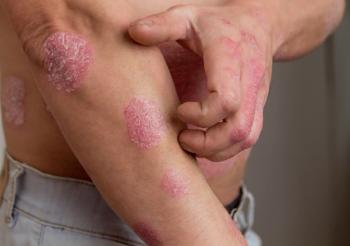
Explore the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in psoriasis management, highlighting their immunomodulatory effects and metabolic benefits for patients.
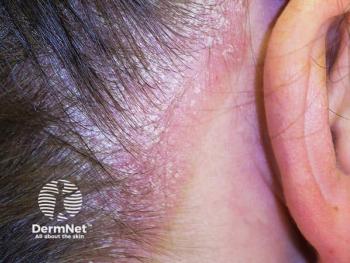
Roflumilast foam shows significant efficacy in treating scalp and body psoriasis, enhancing patient adherence and quality of life in a recent clinical trial.

Guselkumab shows high effectiveness and safety in treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, enhancing quality of life in real-world Korean patients.

Younger patients with moderate to severe psoriasis exhibit risky sun exposure behaviors, raising concerns about tanning addiction and skin cancer risks.
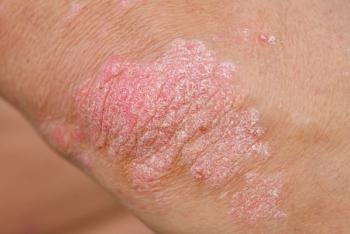
VYNE Therapeutics paused its VYN202 trial for psoriasis due to an FDA-issued clinical hold.
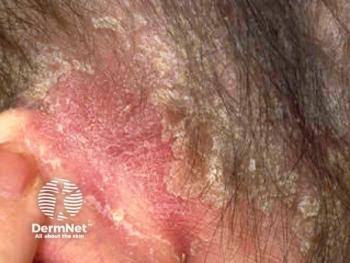
Continuity with a known physician and rapid response times significantly increased patient willingness to use teledermatology.

Eichenfield discusses safety, lab monitoring, and treatment positioning of icotrokinra in adolescents with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
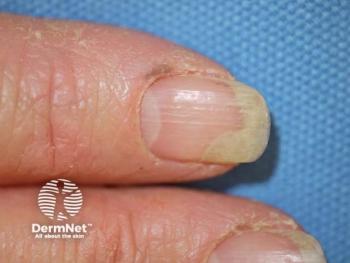
Trials often exclude high-risk patients, limiting the real-world relevance of their safety findings.

Panelists discuss how medical professionals anticipate new IL-17 inhibitor data, particularly from head-to-head trials like BE BOLD. Interest is growing in sonelokimab, an IL-17A/F nanobody (Papp, 2021). Further research is needed on long-term efficacy, safety, and optimal patient selection.

Panelists discuss how head-to-head trials in psoriasis provide direct efficacy and safety comparisons between IL-17 inhibitors and other drug classes. Studies like BE RADIANT, BE VIVID, and IXORA-R highlight bimekizumab’s and ixekizumab’s superiority over secukinumab and ustekinumab. CLARITY and COBRA compare IL-17 to IL-23 inhibitors, while IMMerge and BE BOLD explore risankizumab’s role. These trials inform treatment decisions by guiding biologic selection based on efficacy, durability, and safety.

Eichenfield discusses high skin clearance and safety in teens with psoriasis, per new ICONIC-LEAD phase 3 data.

A recent study reveals that women with psoriasis are more likely to discontinue biologic treatments, including IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors, due to adverse events and treatment dissatisfaction.

Subcutaneous methotrexate may offer improved efficacy and patient adherence in psoriasis treatment, though it comes at a higher cost.

Panelists discuss how long-term data confirm the sustained efficacy and safety of IL-17 inhibitors in psoriasis. Secukinumab (Bissonnette, 2018; Langley, 2022) and ixekizumab (Blauvelt, 2021) show durable PASI responses over 5 years. Brodalumab’s 5-year pharmacovigilance (Lebwohl, 2024) and 120-week data (Puig, 2020) support its long-term use. Bimekizumab’s 4-year data (Blauvelt, 2024; Gordon, 2024) demonstrate continued efficacy, with 5-year results anticipated at AAD 2025.

Panelists discuss how when prescribing an IL-17 inhibitor, key safety considerations include infection risk (particularly tuberculosis and fungal infections), inflammatory bowel disease exacerbation, allergic reactions, neutropenia, immunogenicity, vaccination timing, pregnancy/breastfeeding status, malignancy history, and monitoring requirements for adverse events.
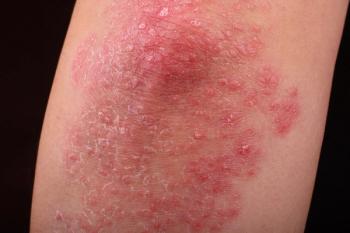
A new subgroup analysis revealed higher rates of clear or almost clear skin at week 16 vs placebo with a favorable safety profile.

Panelists discuss how IL-17 inhibitors are generally well-tolerated, but common adverse effects include infections, particularly candidiasis, and potential increased suicidal ideation risk. Patients should be informed of candidiasis risk, especially with bimekizumab (Gordon, 2022), and monitored for mood changes, as IL-17s and IL-23s may impact mental health (Blauvelt, 2023). Open discussions help assess risks while ensuring treatment benefits.

Panelists discuss how IL-17 inhibitors are considered for plaque psoriasis based on disease severity, comorbidities, and patient preference. Selection factors include efficacy, safety, access, and cost. Clinical trial data guide choices, but real-world factors impact use. Dosing varies: secukinumab (300 mg weekly for 5 weeks, then monthly), ixekizumab (160 mg at week 0, then 80 mg biweekly for 12 weeks, then monthly), brodalumab (210 mg weekly for 3 weeks, then biweekly), and bimekizumab (320 mg every 4 weeks for 16 weeks, then every 8 weeks). Dosing and device options influence prescribing decisions.

Unlike biologics, nonbiologic systemic therapies showed a neutral or slightly increased cardiovascular risk, raising concerns about their long-term safety.

Positive changes in DLQI scores were observed after 4 weeks of therapy as well as the 6-month follow-up.