
A balanced approach to dermatologic care involves using steroids for flare-ups and switching to non-steroidal options for maintenance.
Maddi Hebebrand is an associate editor of Dermatology Times and joined the MJH Life Sciences team in May 2024. She attended Baldwin Wallace University, studying Media Production and Film, and received her Masters in Digital Media from Ohio University. When she's not writing, Maddi loves to read, attend concerts and spend time with her family.

A balanced approach to dermatologic care involves using steroids for flare-ups and switching to non-steroidal options for maintenance.

Chilukuri said devices should be user-friendly even in solo practice settings to maximize efficiency and usability.

Catch up on coverage from the second day of the 2025 South Beach Symposium held in Miami Beach, Florida.

Traditional descriptions often cater to lighter skin, necessitating updates to better serve diverse populations.

Advanced wound healing techniques, including exosomes and polynucleotides, can enhance post-procedure recovery and reduce pigmentation issues.

Nanette Silverberg, MD, discusses new treatments for pediatric vitiligo, including JAK inhibitors and surgical advancements.

Proper nutrition and nutraceuticals can help to manage skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis.

A patient-centered approach ensures that hair loss treatments align with individual goals and medical history.

His presentation at South Beach Symposium will feature Zirwas’ insights on JAK inhibitors, eczema treatments, and emerging therapies.

Goldberg noted combination treatments that integrate radiofrequency, ultrasound, and muscle stimulation could improve patient outcomes.

Catch up on coverage from the first day of the 2025 South Beach Symposium held in Miami Beach, Florida.

“The most important tip as a physician, when you talk to the patient, sit down. Even if you sit down for 5 minutes, it's worth almost 5 hours,’ Leon Kircik, MD, said in his interview with Dermatology Times at SBS 2025.

Nada Elbuluk, MD, MSc, emphasizes that medical treatments remain first-line for vitiligo, but stable cases may benefit from surgical options.

Ablon covered all aspects of getting involved in clinical research, such as budgeting, recruiting, and analyzing data.

According to Silverberg, emotional resilience, social support, and purposeful activities help adolescents cope with acne-related stress.

Nanette Silverberg, MD, highlights new dermatology advancements and the significance of conferences like MOPD in shaping the future of treatment.

Dermatology Times staff will be onsite covering SBS 2025 with expert insights, interviews, and breaking news.

In an interview ahead of the main event, Ablon shared her excitement for SBS and listening in on presentations from industry leaders.

We want to know: Will you be attending the symposium in Miami Beach this week?

The drug, a JAK inhibitor, met all primary and secondary endpoints in a phase 3 trial for adolescent CHE.

Following his presentation at Winter Clinical Miami, Del Rosso spoke to Dermatology Times about the current treatment landscape of psoriasis.

In his presentation at Winter Clinical Miami, Del Rosso covered a variety of topics including refractory pediatric vitiligo.

Biologic coordinators play a key role in managing insurance approvals and ensuring coverage details are confirmed quickly, often within 48 hours.

Explore the top headlines of the week including innovation in scalp treatment, therapeutic updates in rosacea, and acne vulgaris insights from James Del Rosso, DO.

In an interview with Dermatology Times, Del Rosso shared the latest in the treatment landscape for patients with Darier disease.

A recent study found standard burn assessment tools often fail to accurately evaluate injuries in darker skin tones, leading to misdiagnosis and delays.

Researchers found that PsA patients prioritize fatigue, sleep issues, and uncertainty, often ranking them higher than doctors do.
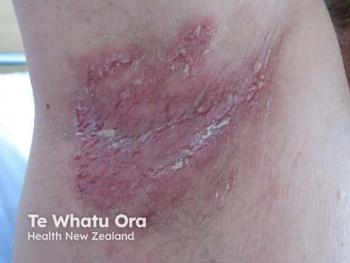
Del Rosso outlined new and off-label therapies for the disease that he shared in his presentation at Winter Clinical Miami.

In an interview with Dermatology Times, Del Rosso gave insight on off-label therapies that could be used to treat granuloma annulare.

The meta-analysis found that HA fillers enhance skin hydration and glow, but do not significantly impact elasticity.