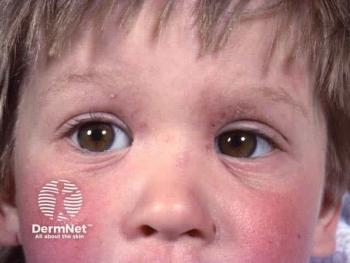
Atopic Dermatitis
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Nektar Therapeutics’ investigational biologic targets the IL-2 receptor complex.

Many patients with severe AD are unaware of newer, more effective treatments.

His presentation at South Beach Symposium will feature Zirwas’ insights on JAK inhibitors, eczema treatments, and emerging therapies.

At the Horizons in Advanced Practice meeting, Lakshi Aldredge, MSN, ANP-BC, DCNP, FAANP, presented a case of a woman aged 35 years with widespread eczematous lesions covering over 50% BSA and severe lichenification.

James Del Rosso, DO, explored the treatment landscape and the importance of regular eye exams for patients with AD.

A new review highlights overall allergen rates among children in the United States between 2010 and 2024.
Researchers analyzed stratum corneum hydration and transepidermal water loss across 15 regions of the skin.
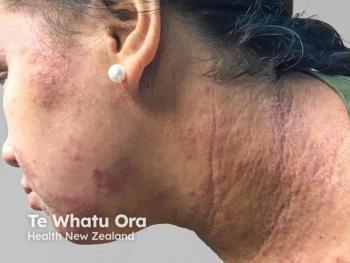
According to a systemic review, both topical and oral antifungal therapies are insufficient for managing the disease.

The use of a pre-gel and cleansing lotion regimen saw an improvement rate of 80% for patients with seborrheic dermatitis.
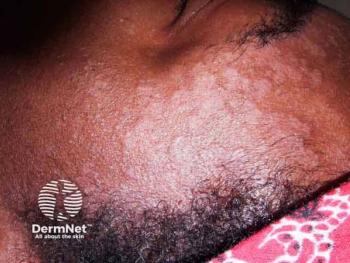
Investigators found strong correlations between certain eating habits, BMI, psychoemotional status, and SD occurrence.

The new partnership will advance the commercialization of small molecule oral STAT6 for patients around the world.

A panelist discusses how recent innovations in topical cream formulations for atopic dermatitis have led to improved efficacy, better tolerability, and enhanced quality of life for patients.

A panelist discusses how combining different therapeutic approaches, such as topical agents with systemic medications, can provide optimal control for patients with severe atopic dermatitis while managing both acute flares and long-term disease maintenance.

A panelist discusses how health care providers can address patients’ concerns about topical treatment side effects in atopic dermatitis by providing education about proper application, expected outcomes, and the strong safety profile of modern topical medications.

A panelist discusses how the choice between systemic and topical treatments for atopic dermatitis patients should be based on factors like disease severity, affected body surface area, impact on quality of life, and previous treatment response.

Rezpegaldesleukin, a novel IL-2 receptor agonist, enters phase 2b evaluation for atopic dermatitis, aiming to advance therapeutic options for this chronic condition.

A study revealed ruxolitinib cream's rapid, lasting benefits in pediatric eczema without systemic safety concerns over a 52-week trial period.

Experts explore innovative therapies, psychosocial impacts, and education strategies for managing atopic dermatitis in a Dermatology Times video series.
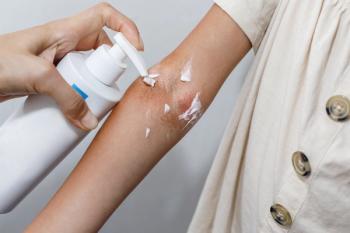
More improved skin hydration and barrier function was observed in moisturizers with anti-inflammatory ingredients, compared to those without.

Real-world data from TARGET-DERM AD revealed that those with both reduced itch and clearer skin had the lowest levels of disease burden.

The panelist discusses how safety data from clinical trials and real-world evidence should guide physicians in prescribing ruxolitinib cream, including patient monitoring protocols and managing potential adverse effects in atopic dermatitis treatment.

The panelist discusses how to effectively communicate with patients about nonsteroidal topical treatment options for atopic dermatitis, including their benefits, proper application methods, and expected outcomes.

The panelist discusses how ruxolitinib treats atopic dermatitis by inhibiting Janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 signaling pathways to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of the skin condition.

Researchers found significant clinical benefits and tolerability with dual therapy for patients unresponsive to dupilumab alone.

A panelist discusses how precision medicine enables targeted atopic dermatitis treatments by matching specific therapies to patients based on their unique disease characteristics and biomarkers