Alopecia
Latest News
Latest Videos
CME Content
More News

Late-Breaking Data: Baricitinib Shows Rapid Hair Regrowth in Adolescents With Severe Alopecia Areata
Anabela Cardoso, MD, provides data on the phase 3 BRAVE-AA-PEDS trial, the largest JAK inhibitor study dedicated to adolescents with severe alopecia areata, at AAD.

Patrick Burnett, MD, PhD, shares key updates expected in 2025 for therapeutics treating atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, and more.

An expert discusses how treatment for alopecia areata begins with topical/intralesional therapies for limited disease and progresses to systemic options for extensive involvement or treatment resistance. Treatment decisions are guided by disease severity, patient age, comorbidities, and treatment goals. FDA-approved systemic agents include ritlecitinib (JAK3/TEC inhibitor) and baricitinib (JAK1/2 inhibitor), which block inflammatory pathways to promote hair regrowth with favorable efficacy, though they require monitoring for potential adverse effects.

A two-set Mendelian randomization analysis revealed a genetic correlation between depression and androgenetic alopecia.

Patients aged 6 to 12 had little to no adverse events and no pharmacokinetic abnormalities were noted.

Clinicians observed a positive relationship between scalp hair regrowth and downstream treatment benefits for patients with alopecia areata.

Compared to minoxidil alone, the combination therapy saw no significant differences in hair count and diameter.
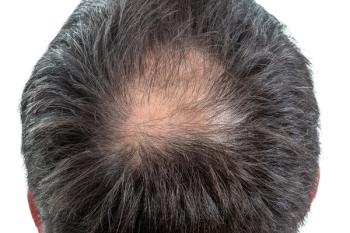
When compared to the placebo, hair growth and quality significantly improved by day 180.

Researchers found patients with conditions like asthma or dermatitis are more likely to develop early, severe, and prolonged forms of alopecia areata.

The analysis findings support the potential use of zinc and vitamin D supplementation in managing alopecia areata.

The 5% dosage showed a 6-fold increase in non-vellus hair count after just 5 weeks.
Itisha S. Jefferson, a patient advocate and medical student, discusses the significance of new ICD-10 codes for CCCA and FFA, improving diagnosis and care.
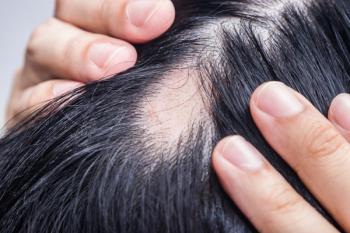
The JAK inhibitor was significantly superior in all safety and efficacy endpoints, when compared to other AA treatment options.

Patients achieved excellent new hair growth and strength when combining PRP with drug therapy after hair transplantation surgery.

The novel systemic review compared results and adverse events associated with various treatment methods.

The phase 2a trial demonstrated the systemic treatment’s tolerable safety profile for patients with chronic and progressive hair loss.

For mild to moderate alopecia areata, topical corticosteroids remain the most frequently prescribed first-line treatment among UK dermatologists.
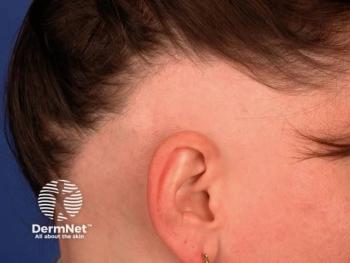
Sun Pharma presented long-term data on Leqselvi 8 mg tablets, showing significant scalp hair regrowth in severe alopecia areata patients.
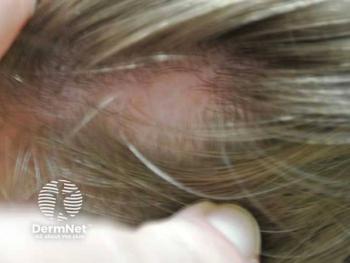
Researchers behind the trial saw a decrease in the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score from 31 to 11.2 after 3 months of treatment with brevilin-A.
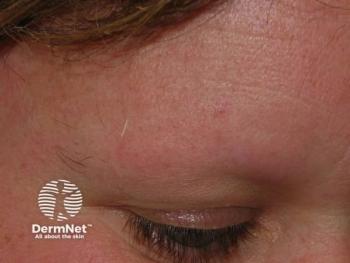
A recent review found hair loss can severely impact self-esteem and body image, leading to social anxiety and emotional distress among affected youth.

Hypothyroidism and Hashimoto's thyroiditis were found to significantly increase the risk of developing AA, unlike hyperthyroidism.
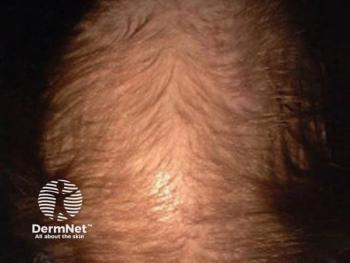
This expert review explores the multifaceted causes of female hair loss—hormonal imbalances, inflammation, nutrient deficiencies, aging, and oxidative stress—and explores non-pharmaceutical interventions.

Arash Mostaghimi, MD, MPH, MPA, provides insights into what clinicians need to know about deuruxolitinib for severe AA.

Understanding comorbidities such as thyroid dysfunction and vitiligo helps to navigate comprehensive care to achieve long-lasting results in alopecia areata treatment.

In his signature Maui Derm NP+PA Fall 2024 session, Shapiro discusses the importance of acting quickly when confronted with a patient who has scarring alopecia.













