Opinion|Videos|March 4, 2025
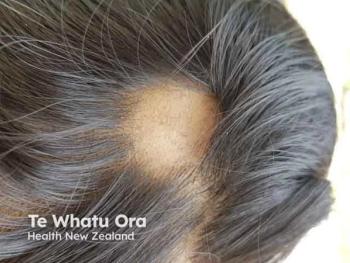
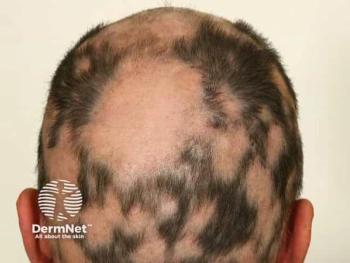
Defining Alopecia Areata Severity and Navigating Treatment Options
Author(s)Susan Taylor, MD, FAAD
An expert discusses how treatment for alopecia areata begins with topical/intralesional therapies for limited disease and progresses to systemic options for extensive involvement or treatment resistance. Treatment decisions are guided by disease severity, patient age, comorbidities, and treatment goals. FDA-approved systemic agents include ritlecitinib (JAK3/TEC inhibitor) and baricitinib (JAK1/2 inhibitor), which block inflammatory pathways to promote hair regrowth with favorable efficacy, though they require monitoring for potential adverse effects.
Advertisement
Episodes in this series

Video content above is prompted by the following:
- Describe your approach to initiating treatment in patients with alopecia areata. At what point do you consider systemic treatment for your patients?
- What factors guide your treatment decisions (severity, patient characteristics, patient expectations, etc)?
- Briefly discuss the systemic agents that are currently FDA approved for alopecia areata, including their mechanism of action as well as efficacy and safety data.
- Ritlecitinib (JAK3/TEC inhibitor)
- Baricitinib (JAK 1/2 inhibitor)
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.
Advertisement
Latest CME
Advertisement
Advertisement
Trending on Dermatology Times
1
Icotrokinra Shows Superior Efficacy Over Advanced Oral Therapies in New Psoriasis Meta-Analysis
2
AbbVie Files for Vitiligo Indication, Putting Systemic Therapy Under Regulatory Review
3
Nutrafol Expands Portfolio with First and Only Hair Loss Supplement for Male Patients 50 and Older
4
Introducing Dermatology Times NP/PA Connect
5