Alopecia
Latest News
Latest Videos
CME Content
More News

At Elevate-Derm Summer, Buchi Neita, MCMSc, PA-C, discussed enhancing dermatologic care for patients with skin of color by recognizing characteristics in common conditions and offered strategies to build rapport with patients.

Nektar Therapeutics advances alopecia areata treatment with FDA's Fast Track designation for rezpegaldesleukin, targeting immune modulation in chronic hair loss.

Amy Spizuoco, DO, FAOCD, shares groundbreaking insights on alopecia treatments and emerging STIs at this year's Elevate-Derm Summer Conference, enhancing patient care.

A first-of-its-kind study reveals artificial intelligence (AI)-driven insights on hair loss trends, highlighting the impact of genetics, hormones, and COVID-19 on alopecia.
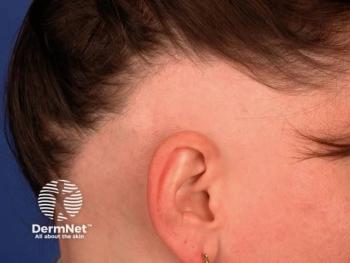
Sun Pharmaceuticals has launched deuruxolitinib (Leqselvi) in the US, offering a new treatment for adults with severe alopecia areata.
A systematic review reveals critical diagnostic gaps in hair loss treatment for patients with skin of color, urging improved training and protocols in dermatology.
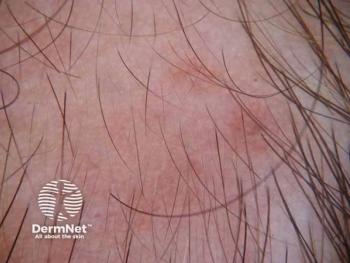
A recent study reveals a significant link between alopecia areata severity and increased risk of atopic dermatitis, especially in adolescents.

From JAK inhibitors to trichoscopy and contact allergy clues, experts at SDPA 2025 shared their top clinical pearls for managing alopecia and hair loss.

David Cotter, MD, PhD, discusses diagnosing alopecia areata and selecting systemic treatments, including JAK inhibitors, from his SDPA 2025 presentation.

PP405 shows promise for hair regrowth in phase 2a trial, with 31% seeing >20% density increase; phase 3 studies are planned for 2026.

Subgroups more likely to respond included women and those with shorter-duration, less-extensive hair loss.

In a real-world study, the combination of Cuticapil stem hair serum and minoxidil reduced shedding and improved hair density.

Explore the significant mental health and socioeconomic impacts of atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata, revealing urgent needs for better support and awareness.

A 10-year study reveals azathioprine's impressive 93% hair regrowth rate in patients with moderate to severe alopecia, highlighting its long-term efficacy and safety.

In a new study, AI-driven personalized treatments significantly enhanced hair growth and scalp health, offering innovative solutions for hair loss management.

Significant unmet needs were found among high-quality validation studies on the internal structure of PROMs specific to alopecia areata.

A novel electrotrichogenic device shows promising results in promoting dense, thickened hair growth for male androgenetic alopecia patients.

The developement of bempikibart offers hope for effective treatment of severe alopecia areata amid unmet medical needs.

The innovative 21-item Hair & Scalp CARE questionnaire is designed to evaluate the psychological impact of hair and scalp conditions on quality of life.
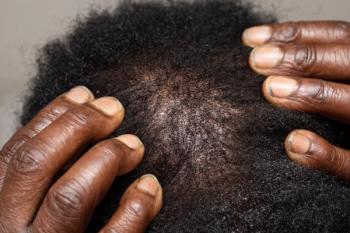
JAK inhibitors show promise in treating alopecia areata among Black patients, highlighting the need for inclusive clinical research and equitable access to therapies.

A recent meta-analysis evaluates the efficacy and safety of various JAK inhibitors for alopecia areata, highlighting 12 mg twice daily deuruxolitinib as the most effective treatment.
At week 24, the proportion of Asian patients achieving significant hair regrowth (SALT ≤20) was substantially higher in ritlecitinib treatment groups than in placebo groups.

According to a clinical trial and in vitro study, TTFE can promote scalp health and hair growth by 96.88% while reducing inflammation.

An expert discusses how alopecia areata affects approximately 2% of the population globally, with onset typically in childhood or early adulthood. Patients often present with autoimmune comorbidities (thyroid disorders, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis) and psychological distress. Diagnostic challenges include differentiating from other hair loss conditions and predicting disease course. Treatment difficulties involve unpredictable responses, lack of standardized protocols, and addressing both physical symptoms and psychological impact.

A two-set Mendelian randomization analysis revealed a genetic correlation between depression and androgenetic alopecia.