Managing Psoriasis in a 72-Year-Old Woman through In-Office Biologic Administration
An expert discusses how treating older patients with psoriasis, such as a 72-year-old retired teacher, requires addressing cognitive decline, dexterity issues, and comorbidities by considering in-office biologic administration and buy-and-bill processes for Medicare accessibility.
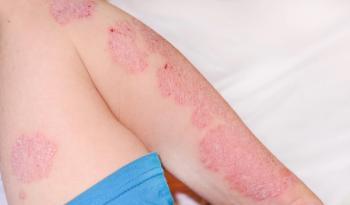
Dr. Noor presents a detailed case study of a 72-year-old retired female schoolteacher with chronic plaque psoriasis affecting 10% of her body surface area. The patient exhibits multiple challenges including mild cognitive impairment, obesity (body mass index, 33), hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and difficulty with topical treatment adherence. This case exemplifies the complex considerations required when treating older patients with psoriasis who face physical limitations, cognitive decline, and metabolic comorbidities.
Managing psoriasis in elderly populations presents unique challenges, with medication access being a primary concern. Noor emphasizes the need for cost-effective, innovative treatments that are efficacious and safe for older patients. The presence of cardiometabolic comorbidities significantly influences treatment decisions, as psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease affecting not only skin but also joints and cardiovascular systems. Research findings demonstrate that biologic therapy, particularly IL-23 inhibitors, can reduce cardiovascular complication risks.
For this older patient case, Noor recommends tildrakizumab as an optimal treatment choice, offering health care provider–administered in-office injections. This approach addresses the patient’s cognitive decline, dexterity issues, and adherence concerns while providing Medicare population access. The buy-and-bill model facilitates treatment by allowing offices to purchase and administer medications directly, streamlining the process for patients with Medicare coverage and reducing prior authorization requirements.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.