Escalating to Biologic Therapy in a 5-Year-Old With Severe Atopic Dermatitis
An expert discusses how a 5-year-old child with severe atopic dermatitis affecting sleep and school performance demonstrates the need for systemic therapy escalation, with dupilumab being an ideal choice given its efficacy for both atopic dermatitis and comorbid asthma.
Episodes in this series

Video content above is prompted by the following:
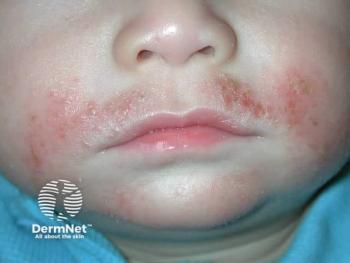
This case study illustrates the critical decision-making process when managing severe pediatric atopic dermatitis that significantly affects a child’s quality of life and development. The 5-year-old patient presented with severe disease covering greater than 10% body surface area, experiencing 4 to 5 nighttime awakenings and demonstrating academic performance issues requiring parental intervention with school officials. The presence of comorbid conditions, including food allergies and mild asthma, further complicated the clinical picture, highlighting the interconnected nature of atopic diseases and the need for comprehensive treatment approaches.
The case demonstrates clear indicators for systemic therapy escalation, including disease severity, significant sleep disruption, and functional impairment affecting school performance. The patient’s additional allergic conditions, particularly asthma, influenced treatment selection toward dupilumab, which offers proven efficacy for both atopic dermatitis and asthma management. Findings from clinical studies demonstrate dupilumab’s effectiveness beginning as early as 2 to 4 weeks after initiation, with substantial improvements typically observed by 16 weeks and sustained benefits over 52 weeks, providing families with realistic expectations for treatment response.
Shared decision-making in pediatric atopic dermatitis requires careful balance between parental concerns and age-appropriate patient involvement. Health care providers must communicate in language accessible to both children and parents, ensuring all parties understand treatment options, expected outcomes, and safety considerations. The excellent safety profile of dupilumab in pediatric populations, with approval for patients as young as 6 months, provides reassurance for families considering biologic therapy. Successful treatment adherence strategies include addressing injection anxiety through techniques such as vibration tools, ice application, and positive reinforcement systems.
Newsletter
Like what you’re reading? Subscribe to Dermatology Times for weekly updates on therapies, innovations, and real-world practice tips.