
POLL: What Topic Do You Most Want Us to Cover at the American Academy of Dermatology Annual Meeting?
Click here to answer our poll and let us know what disease states, topics, and research you most want to see news about throughout the conference.

Click here to answer our poll and let us know what disease states, topics, and research you most want to see news about throughout the conference.

Read more on what you can expect at this year’s AAD meeting and how to navigate all the opportunities.

Following the announcement of Valisure's findings related to benzene and benzoyl peroxide acne products, Dermatology Times spoke with David Light, co-founder and president of the laboratory behind the report, to discuss the findings, the role of stability testing requirements, and quelling fear-filled online discourse.

We've rounded up commentary from trusted dermatology experts who expressed enthusiasm and excitement for the biggest dermatology meeting of the year.

The organization celebrates 2 decades of leading awareness, research, education, membership, and advocacy for clinicians and patients with skin of color.

Among the many sessions to be held at the American Academy of Dermatology Annual Meeting in San Diego, California, several Dermatology Times Editorial Advisory Board members are preparing to share their knowledge and insights.
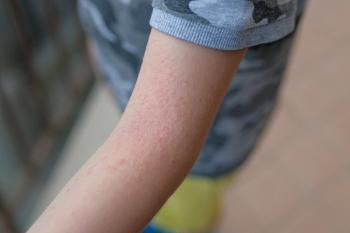
Alphyn’s first-in-class therapeutic is designed to treat the immune system component, and more specifically the bacterial component, of AD.

In our March publication, Winter Editor in Chief Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, delved into the growing concern of benzene in personal care products. This commentary becomes all the more important in light of the recent findings of high levels of benzene in acne products.

There are several events in conjunction with AAD featuring opportunities for dermatology clinicians to gain CME credit, network, explore career options, and gain pearls to put into practice.
In addition to the announcement of positive data, Apogee said the trial has already exceeded its objectives ahead of schedule.

Researchers Eric Sanfilippo, BS; Leslie Castelo-Soccio MD, PhD; and Anna Yasmine Kirkorian, MD, discussed the ethical considerations and methods of removal of unwanted hair in young patients.
Niacinamide is a versatile skincare ingredient that effectively targets acne, age-related issues, hyperpigmentation, and atopic dermatitis, writes Anjeza Fero, PharmD, RPh.

In this week’s Pointers With Portela, the 208SkinDoc answers common hair loss questions.

Educating the public on how physician assistants transform health care through expertise and empathy increases patient outcomes.

High levels of the chemical benzene, which has been linked to cancer, were detected in numerous consumer acne products, including from major brands such as Proactiv, Clinique, and more.

This week’s collection of the latest dermatologic studies covers the connection between dermatology and COVID-19, the efficacy of topical 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod in treating cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in situ, challenges in treating chronic spontaneous urticaria, and patient satisfaction of treating recalcitrant keloids with intralesional bleomycin and lidocaine.

The botanical blend also demonstrated potential to protect the skin from free radical damage on a cellular level, the study found.

The study will evaluate rezpegaldesleukin and its effect on Severity of Alopecia Tool scoring by the conclusion of a 36-week period.

Nitin Joshi, PhD, shared CAGE Bio’s development of CGB-500 and why phase 2 EASI scores have the company’s scientific advisory board optimistic.

The approval also marks the first and only approved HA dermal filler approved in the US for use in the upper face.

It is always essential to have clear communication regarding expectations at your new practice.

Factors including disease duration, treatment response, and mental health were listed as crucial factors in severity and treatment.

Test your knowledge on the AAD's recommendations for phototherapy, monoclonal antibodies, JAK inhibitors, and systemic therapies in the latest guidelines.

As someone who practices dermatology, it can often be difficult to determine if any of these new skin care trends are efficacious.

We want to know: Will you be attending the conference in San Diego later this week?

Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, gives a sneak peek of what to expect in atopic dermatitis education at the 2024 American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Meeting in San Diego, California March 8-12. Since the last meeting, the AAD has released new guidelines to treat the condition.

Psoriasis is linked to a heightened risk of cardiovascular disease, necessitating proactive screening, collaborative care, and consideration of potential impacts of psoriasis treatments on cardiovascular health.

Keep up with the latest headlines in dermatology from the past week, including a physician working to address the overlooked issue of skin diseases in Black patients, the initiation of a Good Laboratory Practice toxicology study for topical treatment DB-007-4, and more.

ICYMI, this week we had news about late-breaking phase 2 data on rilzabrutinib for CSU, data from the BRAVE-AA1 and BRAVE-AA2 trials for alopecia areata, Rare Disease Day insights, and more.

In this week’s Pointers With Portela, the 208SkinDoc discusses dangerous skin care marketing to watch out for.