
A recent review by the National Psoriasis Foundation's medical board suggests that adults with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may use dietary interventions to supplement standard medical therapies to reduce disease severity.

A recent review by the National Psoriasis Foundation's medical board suggests that adults with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may use dietary interventions to supplement standard medical therapies to reduce disease severity.

Adalimumab trials in psoriasis show no new safety signals in nearly 5,500 patient-years (PYs) of exposure, shows a review in the British Journal of Dermatology.

The superiority of risankizumab over ustekinumab and placebo in two phase three psoriasis trials supports the value of targeting interleukin (IL)-23 alone over IL-12 and IL-23, according to study authors. The publication appeared online in the August issue of The Lancet.

Biologic efficacy may not wane under previous exposure to biologic treatments, study shows.

A review of complementary and alternative medicines used by more than 51 percent of patients with psoriasis, shows that indigo naturalis, curcumin, dietary modification, fish oil, meditation, and acupuncture may be effective in some patients, but proceed cautiously investigators say.

Ortho Dermatologics announced in August that it resubmitted a new drug application to the FDA for DUOBRIITM1, a lotion for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.
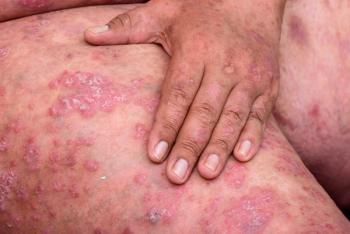
In this slideshow, we highlight some of this year's clinical advances in psoriasis and plaque psoriasis.

A JAMA Dermatology study shows that adherence to a Mediterranean diet high in anti-inflammatory nutrients may lessen psoriasis severity.

The prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis worldwide appears to be around 20 percent, shows a meta-analysis published in JAAD.

As dermatologists become increasingly aware of comorbidities associated with psoriasis, questions of associated malignancy risk remain. Dr. Megan Noe emphasizes the need for skin cancer checks.

For psoriasis in difficult locations including the scalp, palms and soles, guselkumab outperformed adalimumab and placebo, shows a study published online in JAMA Dermatology.
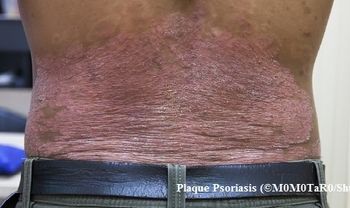
Ustekinumab has a higher drug survival rate than adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab, confirms a study of plaque psoriasis patients published in the Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery.

A new study advises selecting biologic therapies for psoriasis based on individual factors such as patients' comorbidities, preferences and clinical situation, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of particular biologic treatments.

This is the first time an IL-23 blocking drug has been shown to improve signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis.

Adalimumab may be effective for plaque psoriasis, but not heart disease and other inflammatory conditions associated with the condition. This study confirms that the inflammatory process is unique and that one treatment may not apply to other inflammatory conditions.


Efficacy and safety outcomes of clinical trials involving biologic psoriasis drugs overstate these drugs' real-world utility, shows a JAMA Dermatology study.

The TNF alpha inhibitor certolizumab pegol has achieved the highest response rates seen in phase three trials of self-injectable biologics for psoriasis, shows a study published in JAAD.

Physicians may want to reconsider goals for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. In this study, physicians describe utilizing treat-to-target with a patient-centered approach to care for symptom relief.

As the list of treatments for plaque psoriasis grows, so does the list of adverse events associated with biologic treatment. In this article, we summarize adverse events associated with common treatments for plaque psoriasis.

Brodalumab most cost-effective with high efficacy for plaque psoriasis, but IL-17 inhibitors as a whole outperform other biologics, study shows.

Twice-monthly certolizumab for plaque psoriasis could prove to be an option for patients who struggle with twice-weekly dosing, a study shows.

"Plaque psoriasis is increasingly recognized as a multisystemic disease whose most common comorbidities include psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, overweight/obesity, inflammatory bowel disease, and depression. The presence of such comorbidities affects the therapeutic choices for clinicians," researchers write in Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery.

A study that compares the safety, efficacy and drug survival of biologics to biosimilars, finds that switching to a biosimilar had no significant impact on drug survival or safe

While there are biologics and systemic agents designed to control the severe form of plaque psoriasis, few treatments work as well in moderate plaque psoriasis. Apremilast may be a game changer.