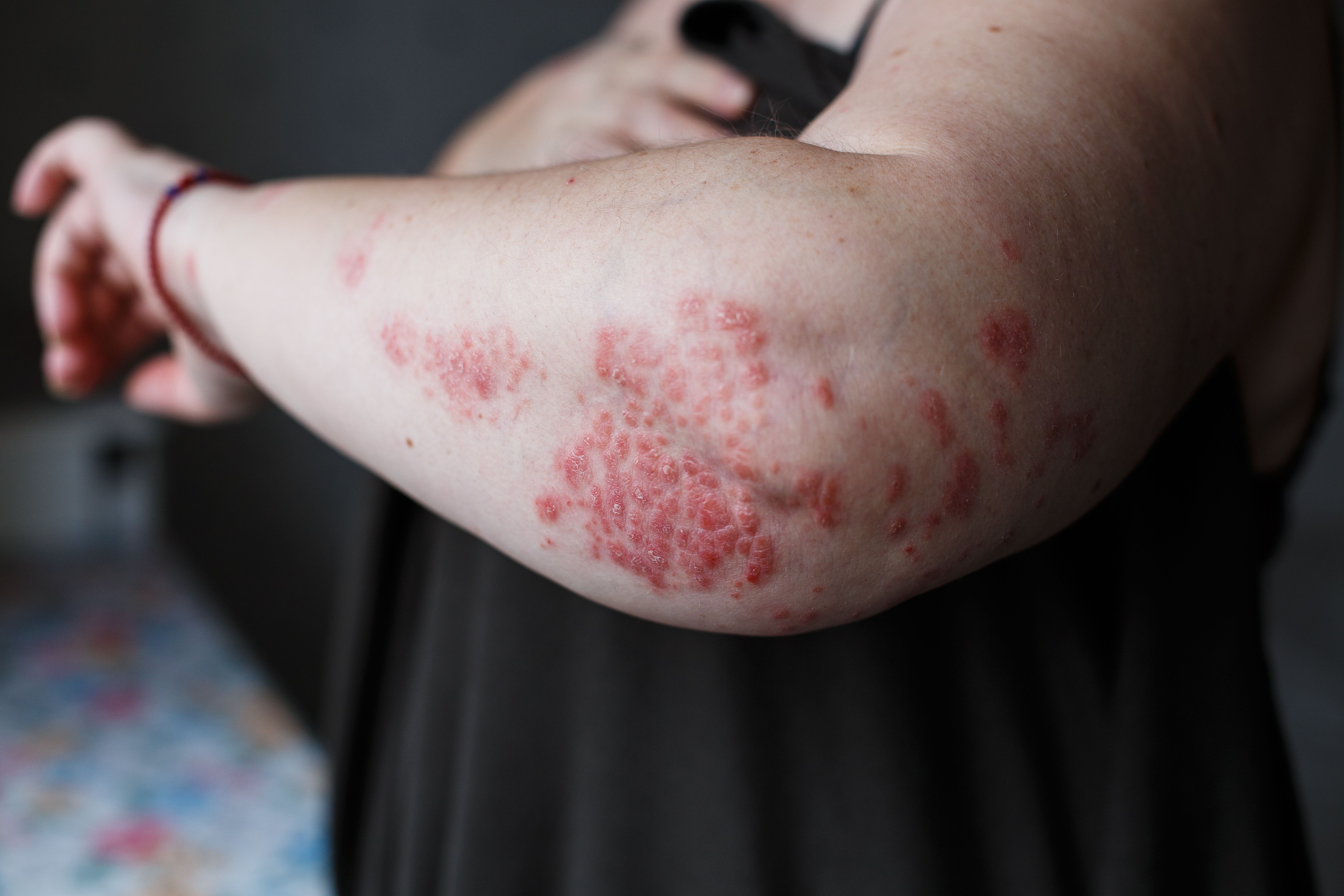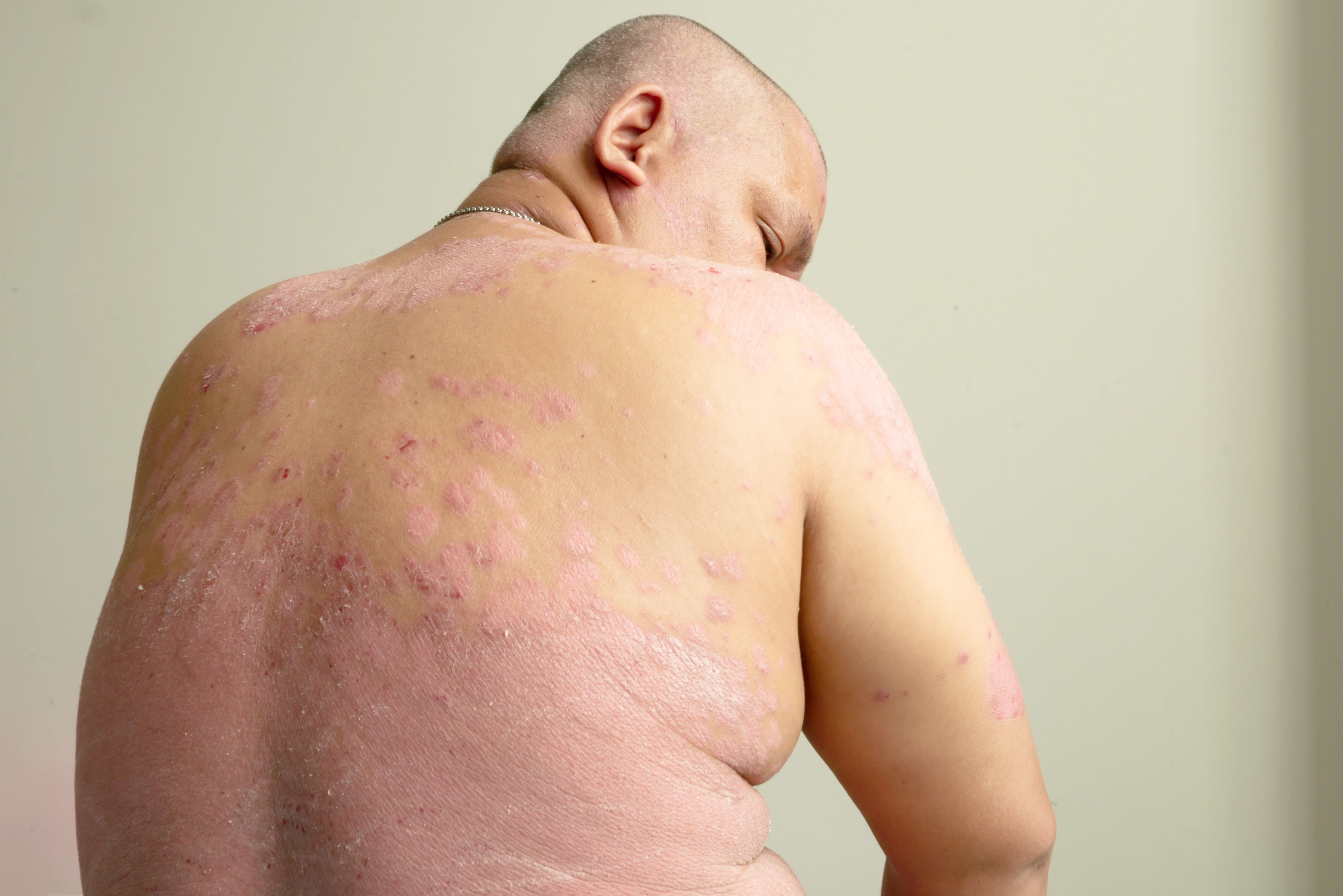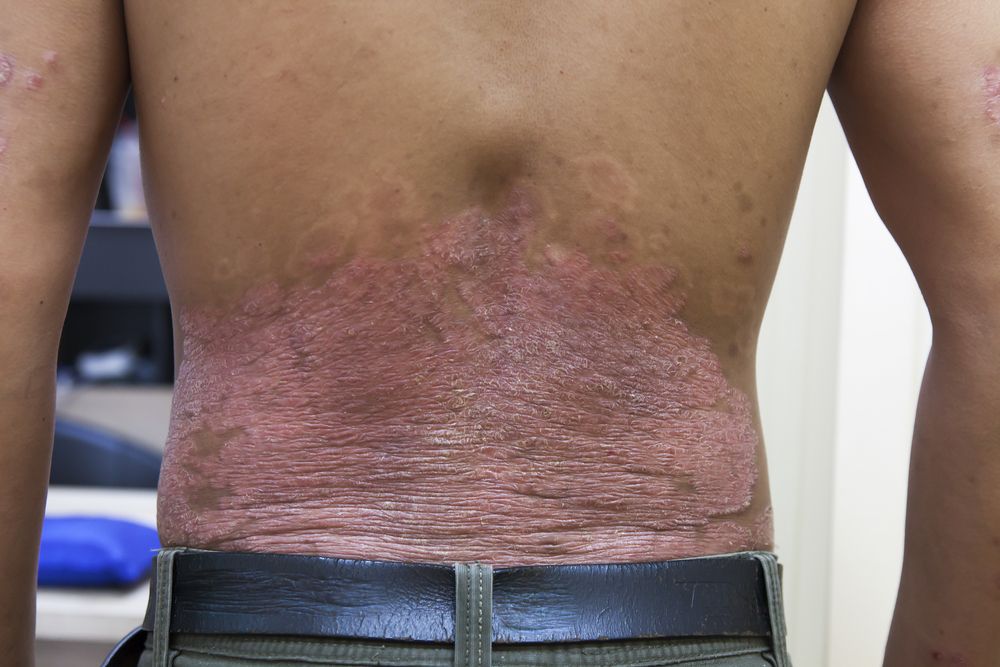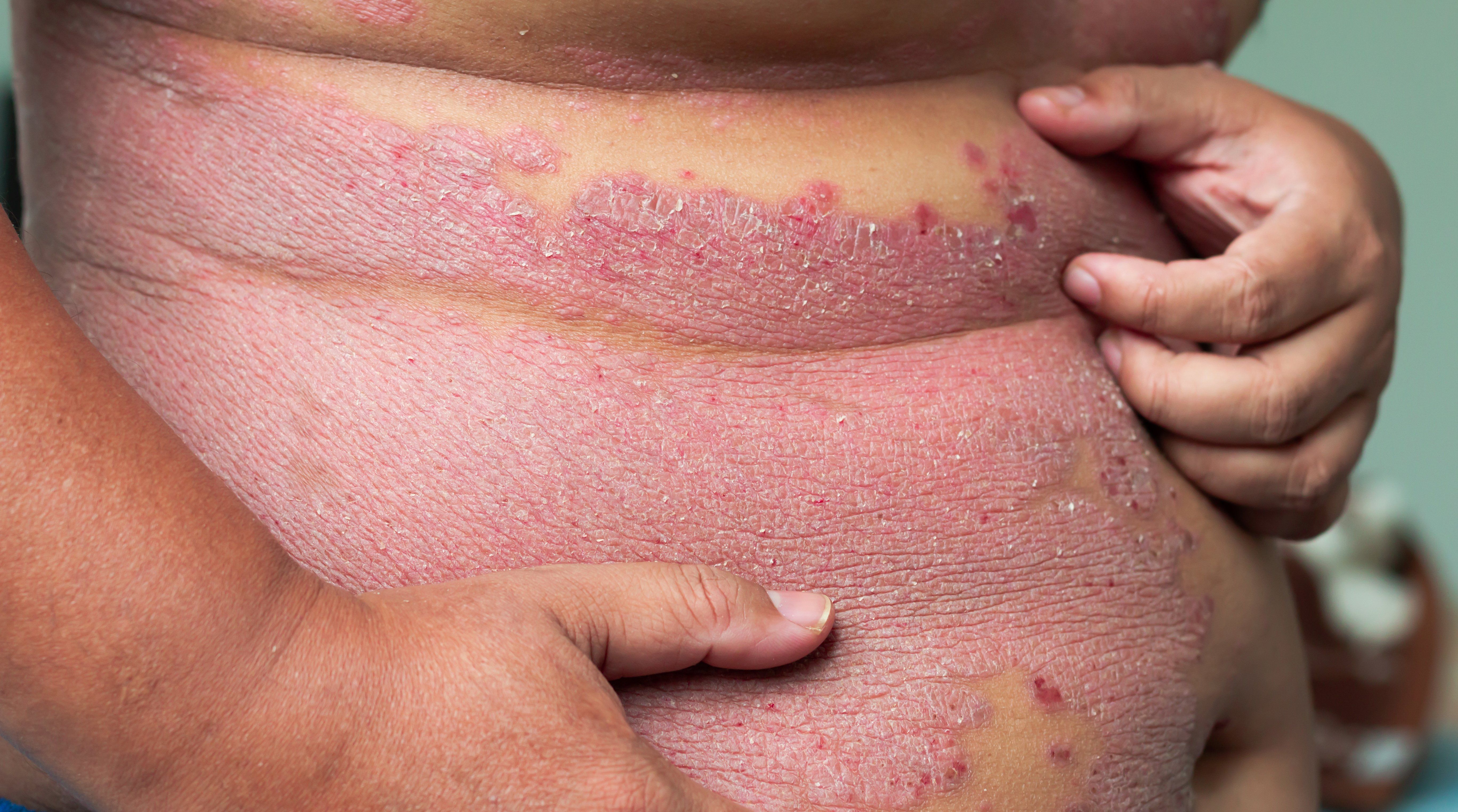
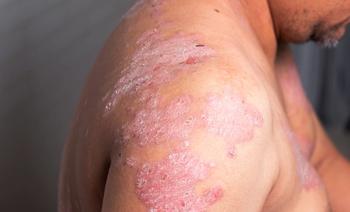
Treatments for Plaque Psoriasis
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can successfully treat the physical symptoms of psoriasis and systemic treatment doesn't seem to provide an extra boost to its effectiveness, a new systematic review and meta-analysis finds.
In psoriasis, many therapies offer roughly the same level of care, but that doesn’t mean any patient will respond well to any therapy. According to Mark Lebwohl, M.D., physicians should consider each treatment option in light of a patient's specific comorbidities.

Why do biologics lose efficacy over time? This physician discusses factors dermatologists should consider when they see this issue in their patients.

Researchers found a significant inverse correlation between ustekinumab levels and PASI scores at week 52, suggesting that drug levels are associated with the change in the treatment response. Measuring ustekinumab levels can have major clinical implications.
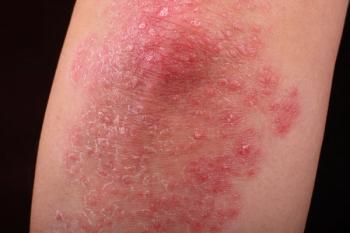
Guidelines suggest that providing a small test dose of methotrexate to patients followed by laboratory evaluation can minimize the risk of serious adverse events associated with methotrexate. This small retrospective study examined whether methotrexate requires a test dose.
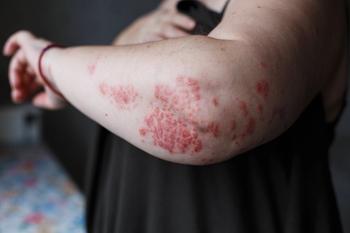
With a crowded indication that includes 14 systemic agents, is there really room for tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2) inhibitors to treat psoriasis? This physician thinks so.
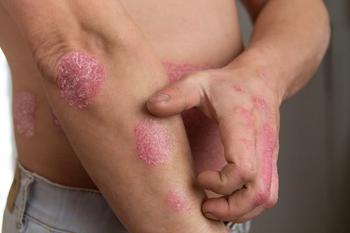
While this new class of medications still has a role in treating psoriasis, this physician says the standard for both their efficacy and safety is very high because of the existing, already very effective systemic therapies available today.

Researchers recently performed a control trial to test the efficacy of BMS-986165 a potent TYK2 inhibitor. Here's what they found.

Researchers at The Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine recently explored the development of a psoriasiform rash in patients with inflammatory bowel disease or rheumatoid arthritis who were treated with TNF-ɑ inhibitors. Learn what they discovered in this article.

A recent study suggests that patients suffering from psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis may have an increased risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease.

Having psoriasis gives a patient a 1.75-fold increased odds of developing ulcerative colitis and a 1.70-fold increased odds of developing Crohn's disease.

Doctors should be vigilant about recognizing the signs and symptoms of patients who may develop ILD in order to prevent catastrophic complications, such as respiratory failure.

Increased mortality described in the first study to review all-cause mortality and cause-specific mortality in patients with psoriasis.

The TNF alpha inhibitor certolizumab pegol (Cimzia, UCB) has achieved the highest response rates seen in phase three trials of self-injectable biologics for psoriasis.
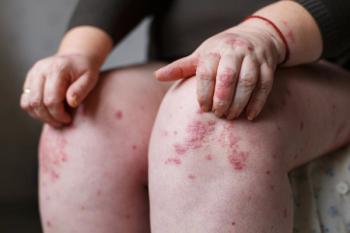
A meta-analysis of 43,643 patients with multiple sclerosis shows that these patients have an increased incidence and prevalence of psoriasis.

The patient-provider relationship in psoriasis care is plagued by various disconnects, a review shows. Decision aids, interdisciplinary involvement may help.

Halobetasol propionate once a week for eight weeks in plaque psoriasis patients was effective, with no adverse events.

It can take weeks to achieve results after restarting biologic treatments that were stopped, study shows.
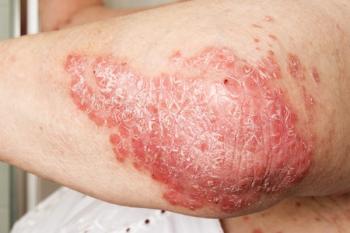
Patients with early-onset psoriasis are less likely than those with late-onset psoriasis to respond to systemic psoriasis treatments, a scientific review shows.

A review of more than 5,000 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who were treated with ixekizumab over three years, shows no unexpected safety signals.

Psoriasis is associated with a host of comorbidities, such as obesity and the metabolic syndrome. In this study, researchers show that fatty liver disease is often the first sign of worsening health.

A novel tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor may provide efficacy comparable to that of currently available biologic agents for psoriasis, without the adverse effects associated with JAK inhibitors, a study shows.

A recent review by the National Psoriasis Foundation's medical board suggests that adults with psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may use dietary interventions to supplement standard medical therapies to reduce disease severity.

Adalimumab trials in psoriasis show no new safety signals in nearly 5,500 patient-years (PYs) of exposure, shows a review in the British Journal of Dermatology.

The superiority of risankizumab over ustekinumab and placebo in two phase three psoriasis trials supports the value of targeting interleukin (IL)-23 alone over IL-12 and IL-23, according to study authors. The publication appeared online in the August issue of The Lancet.