
Recent literature shows associations between rosacea and numerous inflammatory gastrointestinal disorders.

Recent literature shows associations between rosacea and numerous inflammatory gastrointestinal disorders.
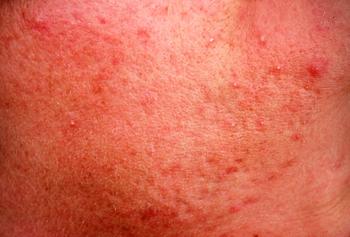
Fluorescence-advanced videodermatoscopy (FAV, Adamo Srl) for characterization of Demodex mites suggests that it can be a useful tool in the clinical evaluation and management of patients with Demodex-related skin diseases.

Investigators assessed results combining oxymetazoline and four different lasers in a recent phase 4 study. Results demonstrate improvement from baseline in Clinician Erythema Assessment (CEA) score.

A variety of new vehicles designed to improve tolerability and cosmetic acceptability are providing rosacea patients with multiple viable treatment options.

A new artificial intelligence-powered diagnostic tool, Ros-NET, was able to accurately identify rosacea, making way for further development of the technology to aid in diagnosis of the skin condition, according to a recent study.

A recent study conducted by the National Rosacea Society reveals more rosacea patients are satisfied with their treatment, but highlights the need for treatment option awareness among older patient populations.
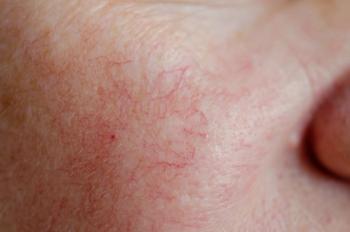
Treatment with a pulsed dye laser followed immediately by intradermal botulinumtoxinA injections appears safe and improved erythema, flushing, burning and pruritus, according to a recent study.

The 21-member global ROSacea Consensus panel developed updated recommendations for rosacea, diagnosis, classification and management to support and promote transition to a phenotype approach in rosacea.

The idea that rosacea is uncommon in darker skinned individuals may be due to under-recognition. Careful clinical examination, a thorough history and biopsy in some cases are needed for accurate diagnosis and differentiating rosacea from diseases that may be more common.

ZILXI (FMX103, VYNE Therapeutics), a 1.5% topical minocycline foam, is now available for prescription for the treatment of inflammatory lesions of rosacea in adult patients.

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted the New Drug Application (NDA) filing for Sol-Gel’s Epsolay, a 5% microencapsulated benzoyl peroxide cream for the treatment of inflammatory lesions of rosacea or papulopustular rosacea.
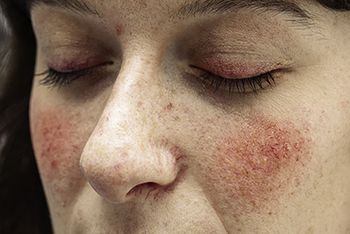
Many patients with rosacea have features that overlap more than one subtype of the condition. A recent publication serves as a compliment to the classification guide with the intention of guiding treatment and management options based on individual patient features.
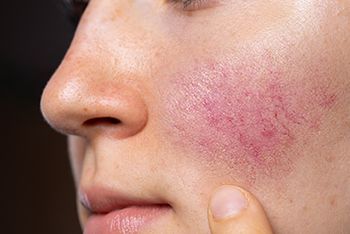
Effects of a specialized skincare regimen for sensitive and redness-prone skin were investigated in an eight-week, prospective, controlled clinical trial enrolling 60 patients with rosacea. The intervention was associated with improvements in objectively measured erythema, rosacea symptoms, and health-related quality of life.
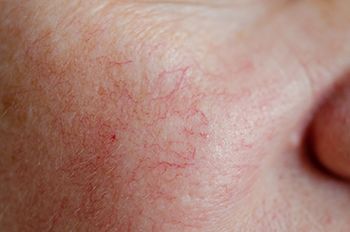
Experts offer insights into the inflammatory pathways involved in rosacea pathogenesis, the putative anti-inflammatory mechanisms of action of treatments for rosacea, and future therapeutic needs.

A study in twins highlights exacerbating factors for patients with rosacea and the importance of the microbiome.

A topical minocycline foam application appears effective and was well-tolerated by patients with moderate-to-severe papulopustular rosacea.

Botulinum toxin may help address erythema and flushing in patients with refractory rosacea, according to data presented by Hema Sundaram, MA, MD, FAAD, at the AAD Virtual Meeting Experience (VMX) on June 12.

A recent study aimed to elucidate the association between variations in the skin’s microbiome and the development of rosacea symptoms.
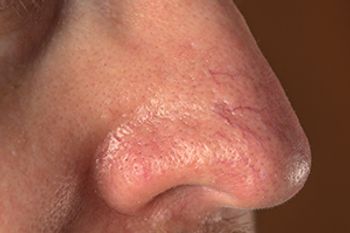

A recent study examined the patient-reported side effects and tolerability concerns associated with azelaic acid foam and metronidazole cream and gel preparations.
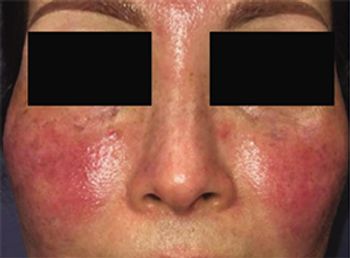
Secukinumab may be safe and effective in patients with moderate-to-severe papulopustular rosacea, a recent study indicates. However, larger, randomized, controlled trials need to confirm benefits.

Recent data sheds light on the pathogenesis of rosacea and outlines treatment options to better manage patients.
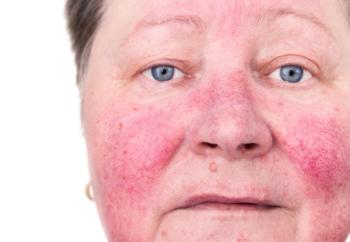
A recent paper discovered that the skin’s microbiota is closely associated with a number of systemic diseases, underscoring the need for clinicians to not only address the microbiota but also consider appropriate antibiotic therapy when contemplating treatment in rosacea patients.

A recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine evaluated the changes seen in the skin’s microbiota of patients following antibiotic therapy to elucidate which organisms might play the biggest role in development of rosacea symptoms.

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved FMX103 (ZILXI, Menlo Therapeutics), a topical 1.5% minocycline foam for the treatment of inflammatory lesions of rosacea in adult patients.