Atopic Dermatitis
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
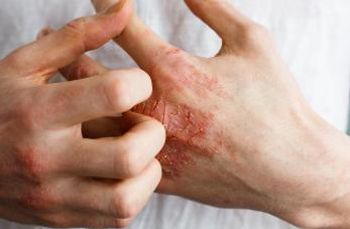
The fully human monoclonal antibody is currently approved in more than 60 countries.
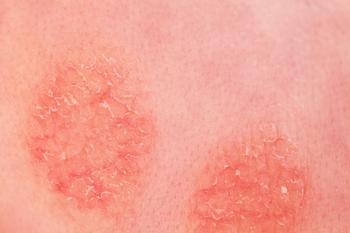
From oat oil to acupuncture to prebiotics, there are many topical, oral, and manual options.

Explore what dermatologic drugs the FDA will decide to approve during July 2021.

The FDA has approved a single-dose pre-filled pen for dupilumab (Dupixent, Sanofi and Regeneron) for at-home administration.

Biologic therapy has proven very useful in treating an increasing number of dermatologic diseases and conditions. However, caution is warranted for patients with chronic infectious diseases.

Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, sits down with Dermatology Times® to discuss recently published results of a phase 3 study evaluating upadacitinib (Rinvoq, AbbVie) as a potential treatment of atopic dermatitis.
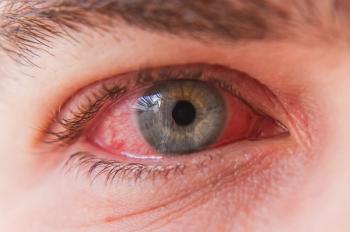
There may be an association between atopic dermatitis severity and diagnosis of ocular disease, such as conjunctivitis.

A new generation of inhibitors take aim at key sources of inflammation.
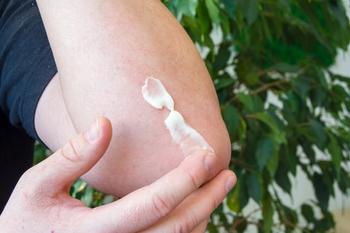
Dermatologists have a variety of topicals to choose from, but other options are on the horizon to add to this armamentarium.

Novel biologics are moving into off-label indications to expand the dermatologic armamentarium for a broad range of inflammatory skin diseases.

A study presented at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience 2021 exhibited new safety and efficacy data for etrasimod as a potential treatment for atopic dermatitis.

Interim analysis of data from the ECZTEND study evaluating the long-term safety, efficacy, and tolerability of tralokinumab for treatment of atopic dermatitis was presented at AAD VMX 2021.

A phase 3 trial produced results on the efficacy of different doses of the JAK1 inhibitor.

Nemolizumab shows positive results according to a recently published post hoc analysis of a phase 2b trial evaluating the drug vs placebo in adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD).

The FDA has decided to extend the priority review period for abrocitinib, a JAK1 inhibitor or moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in patients 12 years and older.

According to objective and subjective measures, children with more severe atopic dermatitis were more likely to report a learning disability.

In this video interview, Linda Stein Gold, MD, discusses her recent presentation at the Inaugural SISD regarding using topicals for atopic dermatitis.

Some strains appear to reduce risk in pregnant women and infants.
Initial rates of common treatment-emergent adverse events from baricitinib 2 mg appear to remain stable or decrease with prolonged exposure.

An investigation examines which infants might require screening before peanut introduction.

Incyte announces the FDA has accepted the NDA for ruxolitinib cream for priority review. Ruxolitinib cream is a topical selective janus kinase (JAK)1/JAK2 inhibitor intended for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.

The limited armamentarium of systemic therapies for atopic dermatitis has already been expanded with the approval of dupilumab. Forthcoming systemic therapies are expected to include a new biologic and three new Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors.

Several universal gaps in diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD) as well as real-world interventions for improvement are the focus of a ground-breaking report.
New treatments for atopic dermatitis offer more options with favorable safety and efficacy.

Spending time around animals as an infant has been suggested as a way to reduce the incidence of atopic dermatitis. An investigation offers some insight.