
Explore the latest dermatology trends for 2026, including innovative therapies for psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and hair loss advancements.

Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, is an associate professor of dermatology and physician-scientist at the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, and Dermatology Times' 2025 editor in chief.

Explore the latest dermatology trends for 2026, including innovative therapies for psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and hair loss advancements.
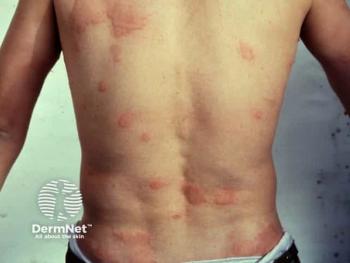
Explore the latest advancements in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) therapies, including innovative treatments and patient-centered management strategies.

Panelists discuss how effective patient onboarding and education enable smooth integration of JAK inhibitors into clinical practice for long-term success.

Panelists discuss how JAK inhibitors demonstrate long-term safety and broad clinical utility across patient populations when guided by careful monitoring.

Panelists discuss how switching from biologics to JAK inhibitors offers rapid, meaningful improvement and restores disease control for patients with persistent atopic dermatitis.

Panelists discuss how the AHEAD recommendations establish structured, patient-centered treatment targets that help clinicians achieve measurable and lasting success in atopic dermatitis management.
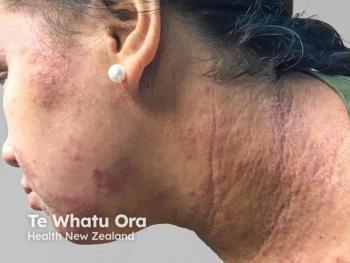
Skin pain in atopic dermatitis significantly impacts quality of life, necessitating its recognition and treatment as a vital symptom for better patient outcomes.

Advances in atopic dermatitis research could bring longer-lasting biologics and improved treatment adherence.

Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, emphasizes how dermatologists can improve outcomes through vigilant skin exams and collaborative care with oncology teams.

Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, urged clinicians to move beyond therapeutic inertia and transition patients to advanced systemic therapies.

Panelists discuss how long-term use of JAK inhibitors provides durable, real-world efficacy and consistent disease control for patients with atopic dermatitis.

Clinicians are now aiming for treatment targets such as NRS 0–1, IGA 0–1, and EASI 90 to define successful AD management.

This October, discover how dermatology and oncology collaborate to enhance breast cancer care and support patients through innovative therapies and teamwork.
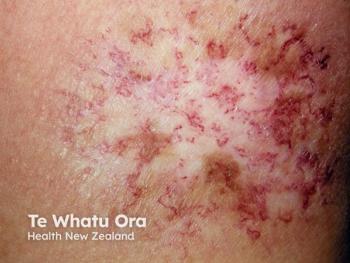
Dermatologists play a crucial role in breast cancer care, enhancing patient outcomes through early detection and innovative research on keratin-targeting therapies.

Galvokamig, a biologic targeting IL-13 and IL-17A/F, demonstrated significant benefits in moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.

New guidelines redefine short-term corticosteroid use in patients with AD, urging safer treatment transitions to advanced therapies for better outcomes.
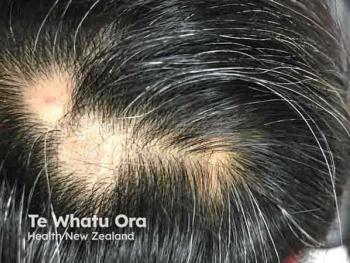
Alopecia areata treatment advances with targeted therapies, improving patient outcomes and access while addressing the emotional impact of hair loss.

An expert discusses how insurance limitations hinder access to newer, more effective acne treatments, emphasizing the need for long-term cost-benefit recognition, while also highlighting the ongoing role of oral antibiotics and the importance of personalized care—especially for adult women with distinct acne profiles.

An expert discusses recent innovations in acne treatment—including the first narrow-spectrum oral antibiotic, an advanced triple-combination topical, and emerging procedural options—highlighting their roles in personalized care, antibiotic stewardship, and achieving long-term therapeutic success.

An expert discusses the preference for narrow-spectrum oral antibiotics in acne treatment due to their favorable safety profile, emphasizing a short-term, combination approach aligned with stewardship principles and the need to balance clinical effectiveness, patient preferences, and access challenges.

An expert discusses the importance of setting clear treatment timelines and goals for oral antibiotics in acne, emphasizing a short-term, combination approach with topicals, careful antibiotic selection based on adverse effects and spectrum, and the benefits of narrow-spectrum agents to support stewardship and patient adherence.

An expert discusses how the primary effectiveness of oral antibiotics in acne lies in their anti-inflammatory properties—especially those of tetracyclines—highlighting their broader immunomodulatory benefits and the importance of patient education to support informed, science-based treatment decisions.

An expert discusses how clinical presentation guides the selective use of oral antibiotics for moderate acne, emphasizing short-term treatment, careful transitions to maintenance therapy, and individualized plans to achieve lasting skin clearance while minimizing antibiotic exposure.
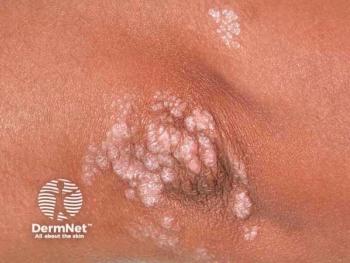
Explore the evolving landscape of moderate psoriasis treatment, emphasizing patient-centered care and innovative therapies for improved quality of life.

An expert discusses how updated guidelines, patient preferences, and insurance access shape responsible oral antibiotic use in acne care, highlighting the importance of stewardship, shared decision-making, and equitable treatment access.

An expert discusses the shift in acne treatment from broad-spectrum antibiotics to targeted and nonantibiotic therapies, emphasizing microbiome preservation, resistance reduction, and personalized patient care.

Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, highlights how dupilumab transforms atopic dermatitis treatment in children, improving health outcomes and quality of life beyond skin symptoms.

At RAD 2025, Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, presented data on amlitelimab and rocatinlimab, highlighting their potential to suppress cytokine signaling and more.

At RAD 2025, Christopher Bunick, MD, PhD, presented 6-month data from the CorEvitas AD Registry, highlighting clinically meaningful skin clearance, itch reduction, and more in bio-naïve and bio-experienced adults treated with upadacitinib.

Acne is increasingly recognized as a chronic condition, affecting diverse populations and demanding innovative treatment strategies and equitable care access.

Published: September 19th 2024 | Updated: September 26th 2024

Published: April 8th 2024 | Updated:

Published: November 1st 2024 | Updated:

Published: October 23rd 2024 | Updated:
Published: May 8th 2025 | Updated:

Published: February 9th 2025 | Updated: