
Men present with melasma too, but there are differentiating factors compared with female melasma patients. Researchers offer insights from a literature review for effectively treating the male melasma patient.

Men present with melasma too, but there are differentiating factors compared with female melasma patients. Researchers offer insights from a literature review for effectively treating the male melasma patient.

A recent study examines the safety and efficacy of picosecond laser as a melasma treatment during a time when lasers are increasingly being used to treat the condition.

When should lasers be used to treat melasma? Mildred López Piñeiro, M.D. provides her insight in our new column on energy devices.

A growing body of evidence supports treating melasma with systemic or intradermal tranexamic acid. But melasma patients often relapse when they stop taking the antifibrinolytic agent, and research on tranexamic acid’s long-term efficacy and safety is limited.
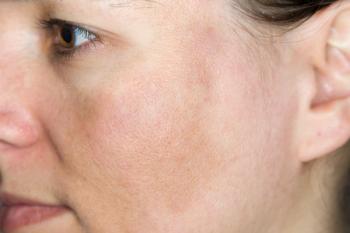
A literature review on clinical evidence for melasma treatments suggests an evidence-based treatment ladder.

A small study examines platelet-rich plasma injection as alternative or adjuvant melasma treatment.

Patients with pigmentary disorders suffer high frequency of psychological disturbances, including anxiety and depression.

New research has shed light on how hyperpigmentation occurs. Experts break down what you need to know in this article.

The methods and products used to combat the day-to-day impacts of melasma has expanded to include tranexamic acid, cysteamine, along others.


From sunscreen in a stick to niacinamide, and a non-hydroquinone, retinol-free skin tone corrector, these are among the promising treatments for hyperpigmentation.

Dermatologist R. Sonia Batra sits down with Dermatology Times for a melasma Q&A.

Experts offer their treatment tips and protocols for melasma prevention and management.

Study reports melasma has a significant negative impact on patient quality of life and self-esteem.
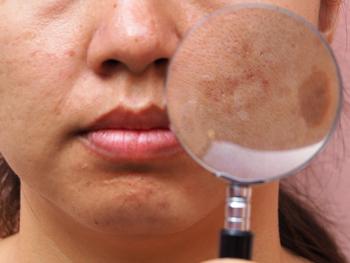
Topical treatments with tranexamic acid offer a safe, effective option for melasma, hyperpigmentation.

Pearl E. Grimes, M.D., discusses the complexities of melasma and the need for a multimodal treatment approach.

Could this new drug delivery system for tranexamic acid optimize melasma treatment? Joel Cohen, M.D., thinks it could be just what the specialty has been looking for.

New consensus conclusions are important, because managing acquired macular pigmentation is a new frontier in dermatology. The article defines terminology and notes the primary feature common to macular pigmentation conditions.

Researchers recently discussed laser and IPLS options for a variety of pigmentary conditions, and provided their recommendations for each one in this review published in European Academy of Dermatology and Venerelogy.

Early diagnosis and appropriate management of hypopigmented skin disorders can improve a patient’s quality of life, halt disease progression and prevent irreversible disability.

Silymarin, derived from milk thistle, could offer the same level of treatment efficacy for melasma with more benefits for patients than the most widely-used therapy, hydroquinone.

Rather than being fueled by a singular desire to be more physically attractive, patients seeking cosmetic procedures are driven by emotional, physical, social and professional reasons, a JAMA Dermatology study shows.

Adding oral tranexamic acid as adjuvant therapy is effective for treating refractory melasma, according to recently published research.

At the recently concluded American Society for Dermatologic Surgery meeting in Phoenix, Arizona, researchers looked at the efficacy of using picosecond lasers to treat melasma, with the aim of reducing adverse effects from current treatment options. The treatment proves to be promising.